Many of us know that 3D printers are machines that create and manufacture objects from computer design models. 3D printers and similar machines follow a series of steps and methods to create a physical object. However, these machines need a material to make an object. In 3D printing, the material used in objects is called filament.
What is Filament?
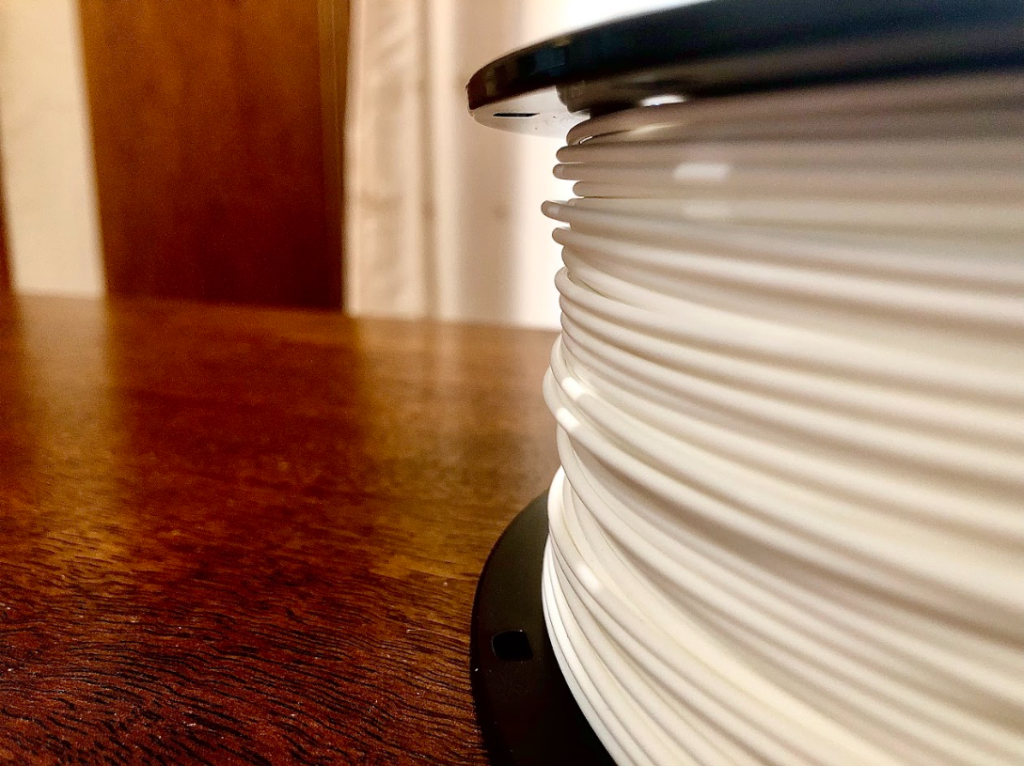

Many materials that 3D printed objects can be made of are classified as filament. In an earlier article, we compared 3D printers to regular paper printers. As described in the first few paragraphs of that article, the 3D printer filament acts as the “ink” of the 3D printer. While an ink printer has the tools and methods to print something, the ink is the main material that the printer uses. Filament works the same way in a 3D printer, without filament, a 3D printer would have no material to print an object.
3D printer filament always has a plastic feel and a wire-like appearance. Filament is almost always rolled around a circular spool or wheel to contain the long strand. While white and black are the most common colors, filament is sold in hundreds of different colors, textures, and even materials, from different manufacturers. This variety of filament types can be used on many different types of printers, although some 3D printers are limited to a few types of filament.
In order to print a physical object, a 3D printer must slowly build up layers of filament until those combined layers reach a specific height. Filament is extruded into the hotend, and out of the 3D printer nozzle. The nozzle continuously places filament in a specific location on the print surface, eventually creating a layer of filament in a certain shape. Hundreds of these layers of filament are placed until the model reaches the goal height.
The Most Common Types of Filament
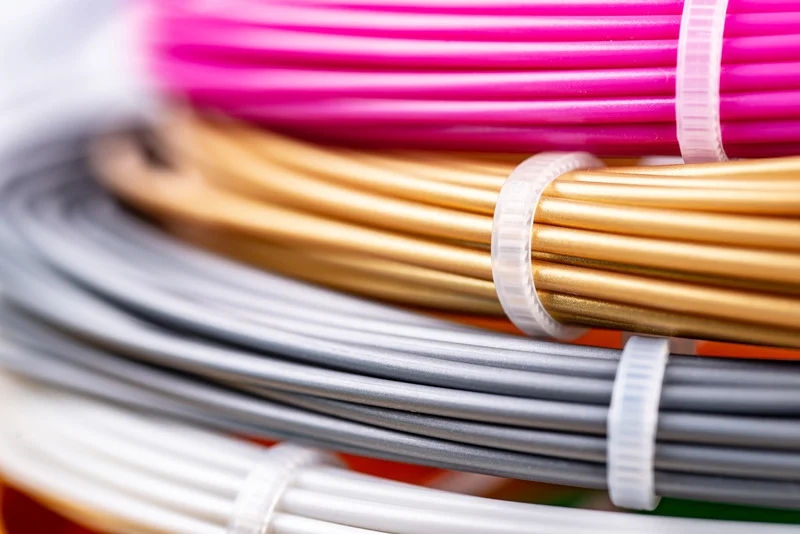

We know that filament comes in many different colors, but there are also different types of filaments made of different materials. These types of filament have their advantages and disadvantages and have different uses and purposes.
PLA Filament
Maybe the most commonly used type of 3D printing filament is PLA filament. PLA filament is classified as a default filament for simple 3D-printed models. PLA’s level of simplicity when 3D printing makes it used by the majority of hobbyists and learners in the 3D printing community.
PLA stands for Polylactic Acid, a natural polymer made from corn starch, sugarcane, and other renewable resources. An object printed with PLA filament will have a hard plastic feel that works well with many decorative and sometimes practical purposes. Many people use PLA filament to create artistic sculptures and models, and many companies use PLA to create an example model for an upcoming project.
While PLA has many great uses, it still has flaws that may cause issues for some print. First of all, PLA-made objects can warp easily when exposed to high heat. Objects made of PLA also struggle with long exposure to different elements. Because of this, PLA-printed objects don’t perform as well when placed outdoors. The outdoor environment has many factors that can cause PLA to degrade, such as sunlight and heat.
As stated before, PLA is the most used filament by hobbyists because of its ease of use. PLA filament can be used on any filament-based 3D printer, whether it’s an open or enclosed printer. It’s also very easy to print with compared to other types of filament, which makes it a great starting point for beginners. Another factor that makes PLA filament so popular is how relatively inexpensive it is, compared to other types of filament. Overall, PLA is the perfect starting point for anyone and everyone new to 3D printing.
ABS Filament
ABS is another one of the most commonly used types of filament in 3D printing. Outside of 3D printing, ABS filament is often used in injection molding, a type of manufacturing of parts and products. Using this filament in 3D printing can have different benefits and disadvantages, depending on a few factors.
ABS stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, a type of thermoplastic polymer with some similar and different properties to PLA. This type of filament has the same hard plastic feel that PLA has. However, there are some differences, as ABS filament can handle more heat and static stress better than PLA. This makes ABS filament a great choice for printing objects with a practical purpose. Most likely, these objects require a stronger and more reliable material.
While PLA filament works with pretty much any 3D printer, the same isn’t true for ABS filament. A disadvantage to using ABS filament is its sensitivity to temperature change. During the printing process of ABS, the filament would require very accurate heat control. Because of this, ABS filament works best with printers that have covers or screens for heat control. Without the correct heat control during printing, the model will most likely warp.
Overall, there are many upsides and downsides to using ABS filament over PLA filament, it ultimately depends on the purpose of the print. PLA is perfect for beginners and decorative prints. Meanwhile, ABS works great for models that go through lots of wear, fatigue, stress, heat exposure, and more. Both filament types cost relatively the same amount. Unless you have a closed printing space, it is advised for beginners to use PLA filament over ABS filament.
ASA Filament
ASA filament is very similar to ABS filament. Both types of filament have very similar characteristics, purposes, and qualities. However, ASA filament is considered by many to be an “improved version” of ABS filament. Many of the downsides to ABS filament that were stated before are solved by using ASA filament instead.
ASA stands for Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate, a 3D printing thermoplastic similar to the others mentioned. We know that ABS filament only works well in 3D printers that have a closed printing environment so that heat control is optimized. ASA filament, however, doesn’t have this restriction.
While printing, heat control is not as much of an important factor as it is for ABS filament. Therefore, ASA has more flexibility when it comes to restrictions of a 3D printer. ASA filament also has more resistance to UV light than ABS does. While ABS can handle lots of heat, static stress, wear, and other outdoor elements, ASA filament can do the same, and better. Another advantage that ASA has over ABS is safety. ABS filament emits lots of fumes while printing, but ASA emits significantly less fumes than ABS does.
The only two disadvantages to ASA filament are the cost and the ease of printing. With the so many improvements ASA filament has on ABS and PLA, it’s not a surprise that the general price is significantly higher than other filament types. ASA is also still hard to print with, similarly to ABS. While ABS struggles with heat control during printing, ASA struggles with sticking to the bed while printing.
Overall, ASA filament is a notable improvement to ABS filament, as it has many of the same characteristics as ABS filament, but better. While price and printability are some downsides to ASA filament, it’s still a great option for someone with an open printer, who wants to print something very strong and secure.
TPU Filament
All the previous filament types stated above are polymers that give off a hard plastic feel. TPU Filament, however, is very different. Instead of printing a hard object. Using TPU filament would result in a very soft and flexible object.
TPU stands for Thermoplastic Polyurethane and comes in many different levels of stiffness and flexibility to buy, based on the shore hardness scale. The shore hardness scale is a range of ratings given to materials describing how hard or soft each material is. A lower rating on the scale means the material is soft, while a higher rating means the material is harder.
ABS and ASA filament are mostly used for models that require lots of strength and stability. Meanwhile, TPU filament is used to make objects that are softer and more flexible. A few examples of objects that would be made using TPU filament include table corner protectors, tires, elastic phone holders, etc.
A downside to using TPU filament for printing is its ease of use. The more flexible and flimsy the filament is, the harder it is to print with. Because of this, most people encourage using a direct-drive extruder system, instead of a Bowden-type extruder system (these systems will be explained in more detail later). Using a Bowden extruder can cause problems with filament clogging in tubes.
How to Set Up Filament to Print
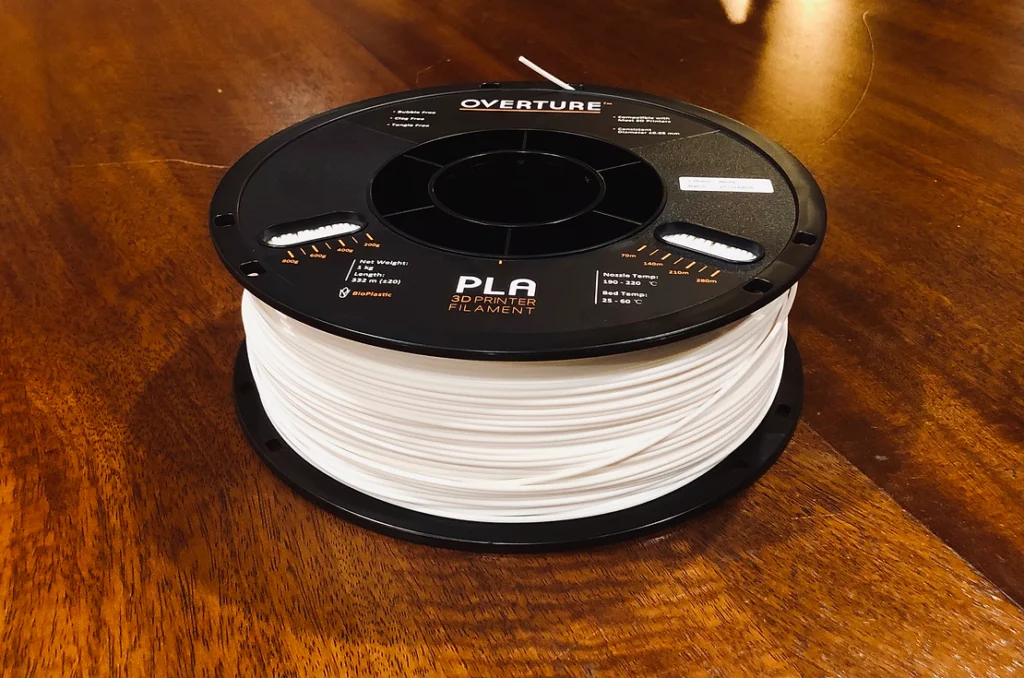

Filament, no matter what type of filament, always comes wrapped around multiple types around a circular-shaped spool. This makes it easy for very long strands of filament (usually almost 400 meters!) to extrude.
When a new spool of filament needs to be used to print, the first step is to insert the end of the filament strand into the extruder. In the picture above, we can see the tip of the strand sticking out of the spool. Before inserting the tip into the extruder, it’s helpful to cut the tip diagonally, to make it sharper. This makes it easier to insert the tip into the printer’s extruder.
Types of Extruders: Bowden Extruder
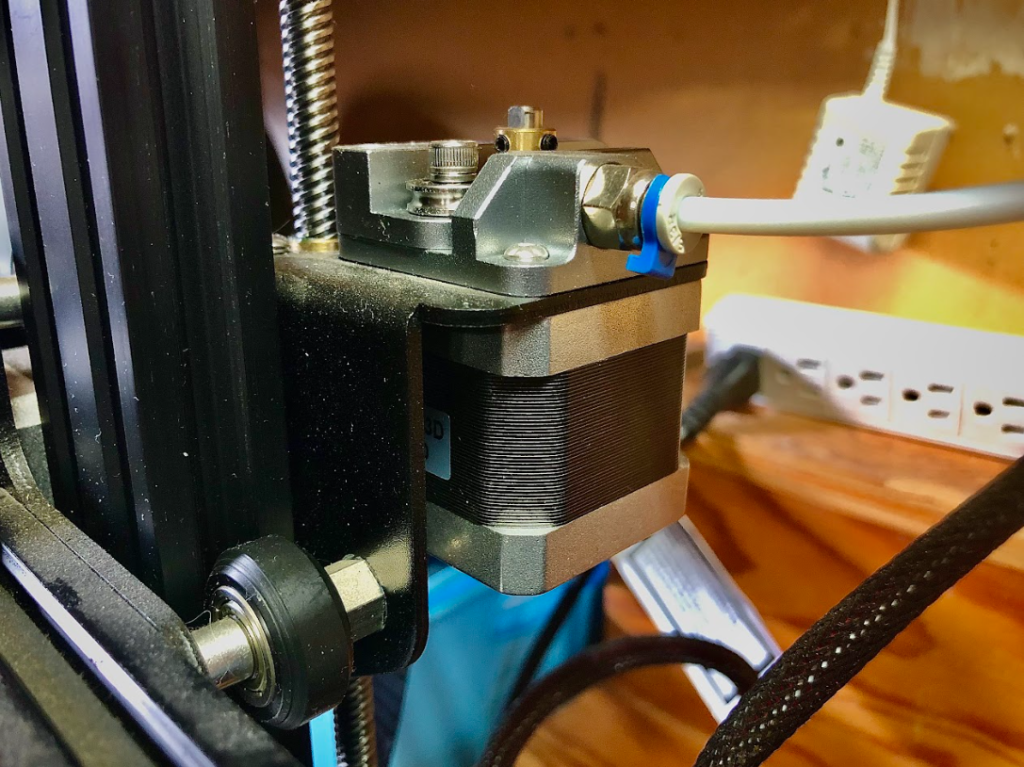

Most 3D printers have extruders that are classified under one of two different extruder types. The first extruder type is the Bowden Extruder. A Bowden extruder is commonly placed on the frame of the printer, separate from the hotend and nozzle. Connecting the extruder and hotend is a long flexible pipe that guides the filament from the extruder into the hotend.
Types of Extruders: Direct Drive Extruder
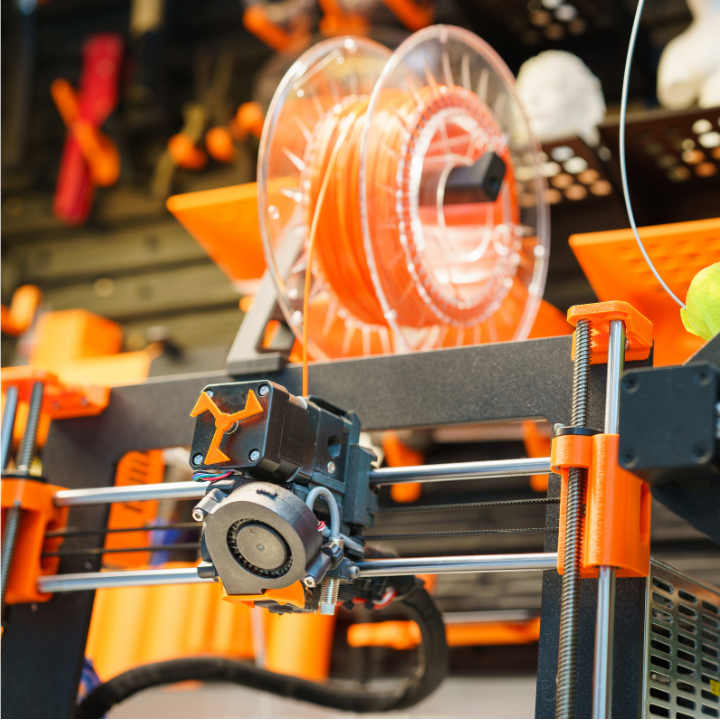

The second most common extruder used in 3D printers is the direct drive extruder. A Bowden extruder is placed separately from the hotend, using a tube or pipe to guide the filament to the hotend. Direct drive extruders are more simple, as they are mounted directly onto the printer’s hotend. This means instead of filament being extruded through a tube, the filament strand moves along with the hotend.
After inserting the strand of filament through either type of extruder, continue pushing the filament through the hotend until you can see some extruding out of the nozzle. Most 3D printers also have a command they can activate that extrudes the filament once inserted into the hotend. After the filament is extruded completely through the nozzle, the filament is all set and ready to print.
Summary

Filament is the building material of all 3D-printed objects and models. Most of the time, filament is a hard polymer that, once printed, has the same characteristics as hard plastic. Different types of filament exist, including PLA, ABS, ASA, TPU, and more. Each type of filament varies in different aspects like strength, flexibility, melting/warping point, and cost. These differences in characteristics allow each type of filament to excel for varying purposes.
Overall, filament is the main foundation of all 3D printed objects, making it one of the most important, if not the most important part of all 3D printing.