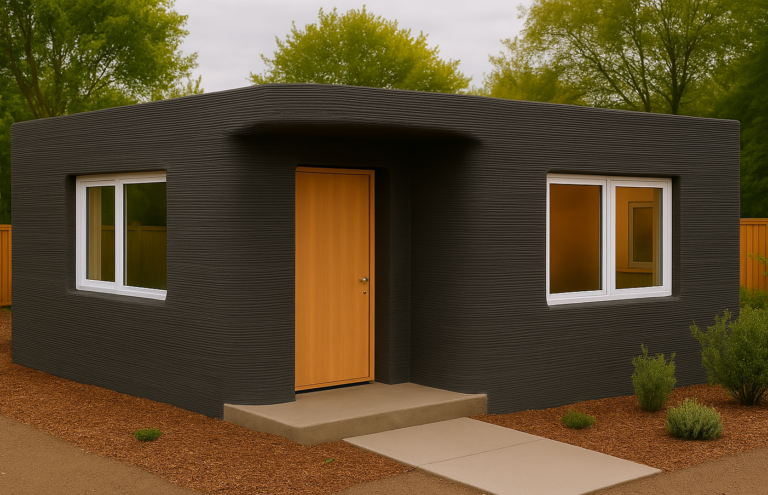
What is a Filament-based 3D Printer?
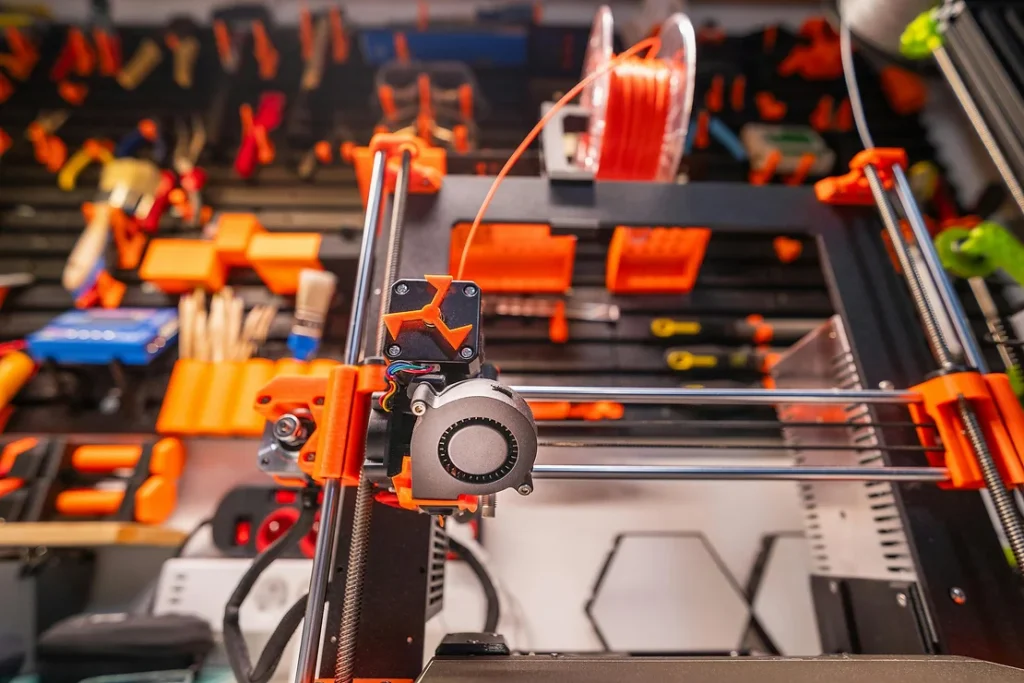

Filament-based 3D printers are the most commonly used type of 3D printer. It uses long strands of plastic “filament” as the main material in models. These long strands of plastic filament are melted down and then carefully placed in a particular pattern on the print bed. The printer then places hundreds of these patterns, one on top of another, creating layers of patterns, and adding thickness to the model.
Filament is most often made of plastic and comes in different colors and materials. The most common type of filament is PLA. Other types of filament include ABS, ASA, TPU, PETG, and others. Each of these filament types has its own properties, including different values of hardness/softness, melting points, durability, resistance to water, and other factors.
What is a Resin-based 3D Printer?
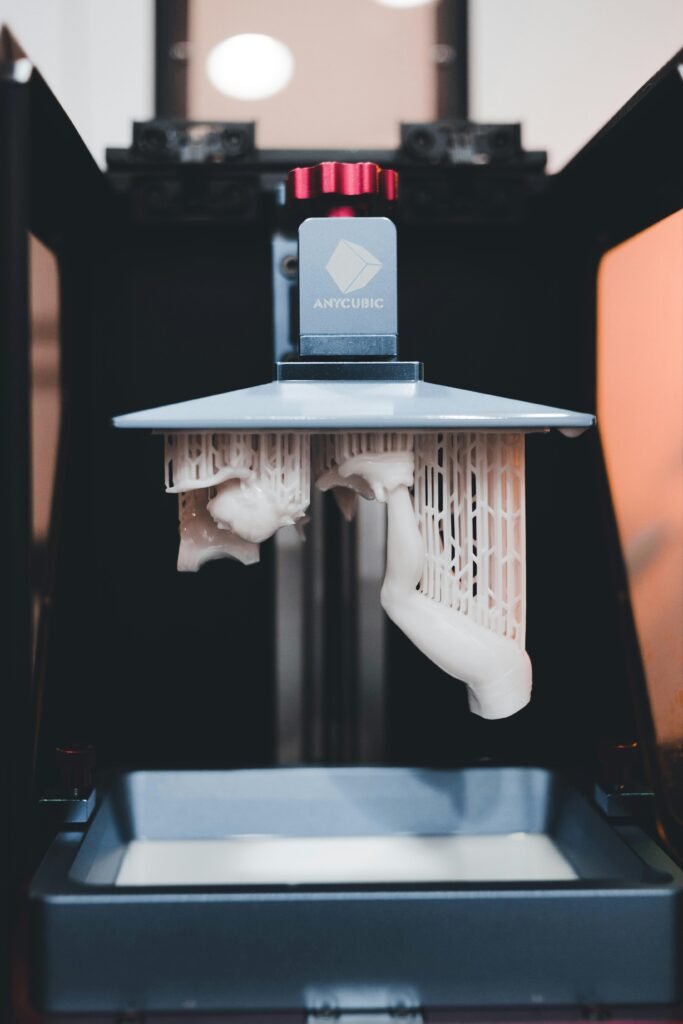

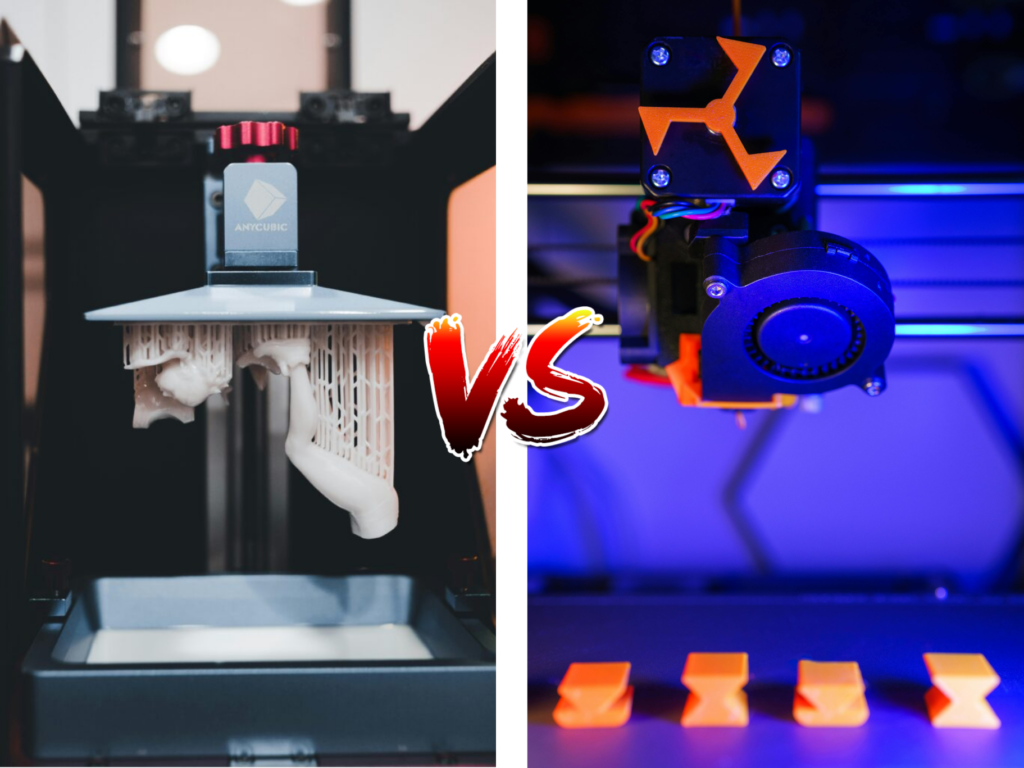
A resin 3D Printer is a type of 3D Printer that uses liquid UV plastic resin as the main material in models. This type of printer is an alternative to FDM or filament-based 3D printers, which use plastic filament instead of plastic resin.
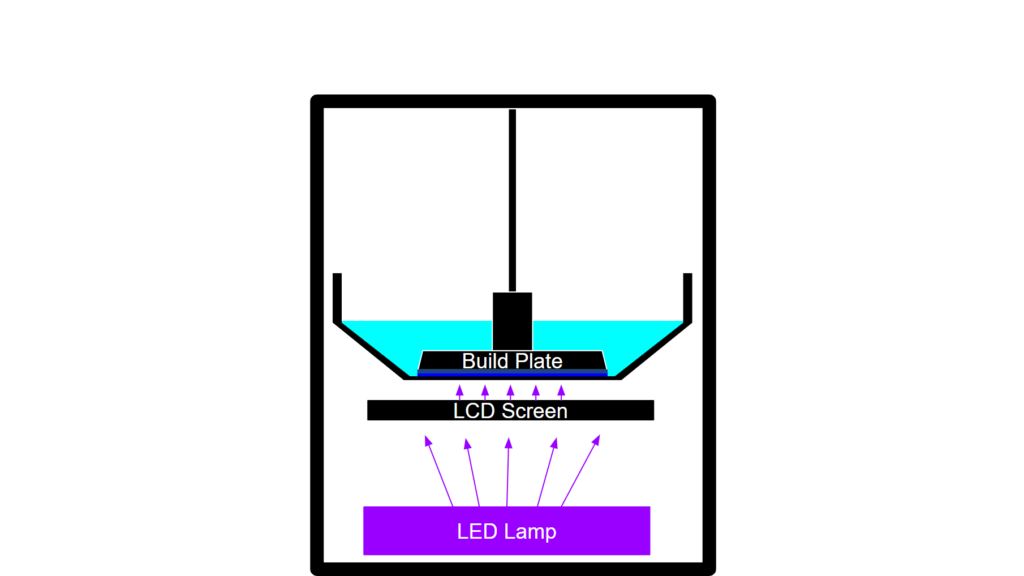
In FDM printing, the filament is melted down and then precisely placed on a print surface in layers to construct a model layer by layer. Resin printers are similar but also different. With each layer, UV light is shined in a particular pattern or shape on the liquid resin. This UV light hardens the liquid resin in the same pattern that was originally shined. This creates the first layer of a resin print. Similarly to filament printers, resin printers build up objects layer by layer on the print surface.
Resin vs. Filament: Ease of use
Resin
The entire process of resin printing is very complicated and could cause many issues for beginners. The process includes filling the resin vat with liquid resin, post-curing and clearing the finished model after printing using isopropyl alcohol, and cleaning up any chemical spills. Resin printing requires more effort, materials, and even skills, in order to complete prints successfully and safely. Overall, resin printers are not easy to use.
Filament
Contrary to resin printers, filament-based 3D printing offers a more beginner-friendly experience. The process is overall easier to understand and easier to complete. The only category that filament printers lack in compared to resin printers is speed. However, filament printers are much simpler and create fewer problems for beginners and hobbyists.
Winner: Filament
Resin vs. Filament: Safety
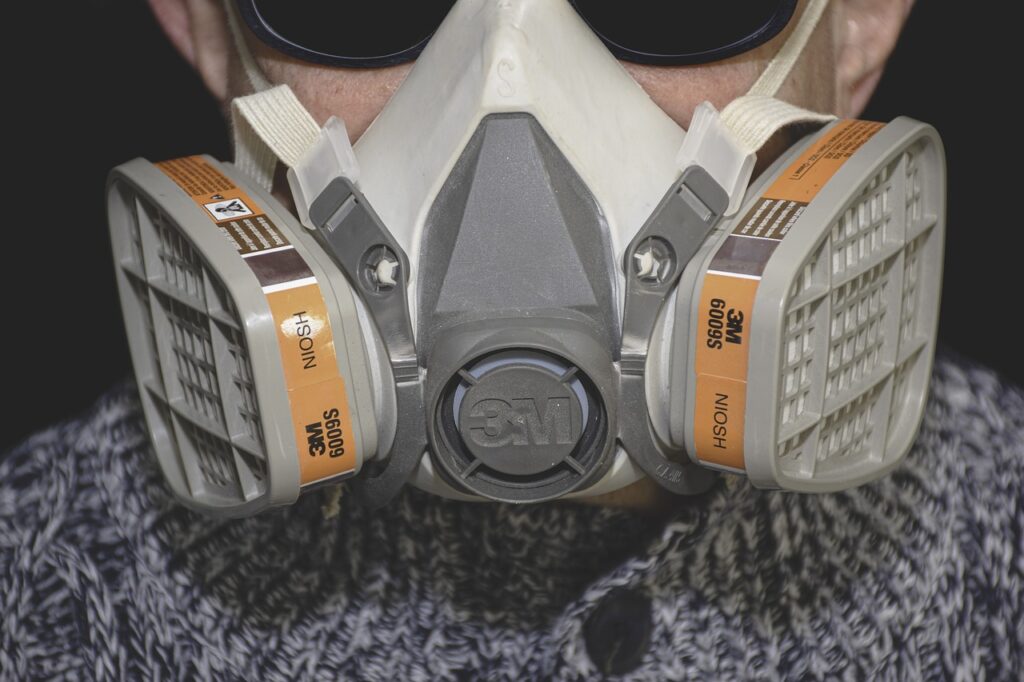

Resin
There are many safety precautions that must be taken with resin printers. For example, resin printing releases lots of harmful fumes during the printing process. Safety materials like gloves, masks, etc. are needed to avoid contact with potentially toxic substances.
Safety issues stem from the fumes released during the print process, and the many chemicals used after the print is finished. One of the most important materials in resin printing is Isopropyl Alcohol, which is used to clean a print of any excess uncured resin. This chemical and other chemicals used in the post-processing stage of resin printing could be harmful if direct contact is experienced. Overall, resin printing can be harmful if the correct precautionary measures aren’t taken.
Filament
Contrary to Resin printing, filament-based 3D printing offers a much safer printing process. However, there are still some potential dangers that must be noted with filament-based 3D printing. These can include minor burns from the heated hotend and some fumes from certain filament types (ABS, PETG,).
While some precautionary measures should be taken to ensure safety, filament-based 3D printing is a much safer process compared to Resin printing. No masks or gloves are required because no harmful chemicals are in use. While harmful fumes can be released, filament printing often produces less fumes than resin printing.
Winner: Filament
Resin vs. Filament: Functionality/Precision/Accuracy

Resin
Resin printing has a completely different process than filament-based printing. These printers use UV light to create more accurate and precise layers. Most miniature sculpture artists use resin printing to make their miniature art to ensure high levels of precision and accuracy. Resin printers also tend to print in many more layers than filament-based printers do, meaning that models will have smoother curves.
Filament
The process of filament-based 3D printing involves placing solid plastic in layers of shapes using a nozzle that extrudes filament. This method is far less precise and accurate than resin printing. Traditional filament-style printing can yield very accurate and precise results, but users often struggle with creating very small, miniature models. It is, of course, much harder for a mechanical nozzle to place filament in the most accurate position, compared to a resin printer’s use of light rays.
Winner: Resin
Resin vs. Filament: Time
Resin
The process of resin printing involves using UV light to harden or “cure” layers of resin in certain shapes. The process of “curing” allows 1 layer to form within seconds, regardless of how big of a shape that layer is. This means hundreds of layers can be created within less than an hour.
However, most models are printed with more layers using resin printing compared to filament printing. This does increase the amount of time it takes compared to traditional filament-based 3D printing, but not a significant amount. Overall, resin printing is usually much faster than filament printing.
Filament
The process of traditional filament-based 3D printing is much slower than the process of resin-based printing. For each layer, a nozzle extrudes filament in a particular path/direction to complete a shape. Depending on the size of a specific layer, this can take a long time or a very short time. It can take many minutes to complete only 1 large layer. Smaller layers can take as fast as 1 minute, however. Overall, filament-based printing can take hours, and for most models is a slower process than resin printing.
Winner: Resin
Resin vs. Filament: Cost

Resin
To get into the hobby of resin-based 3D printing there are many things that need to be purchased. First of all, the entire resin printer is very expensive, many of them being more than a thousand dollars. After buying the actual printer, you also have to buy the main material: liquid UV resin, which is also very expensive (20 dollars per bottle).
While the printer is a one-time investment, resin is something that you have to purchase multiple times and will continue to take funds from your savings. Users must also pay for isopropyl alcohol, damages to the printer, trays, screens, etc. Overall, it is a very large investment, both in the short and long run.
Filament
To get into the hobby of filament-based 3D printing, the first thing that must be purchased is the actual 3D printer. Beginner printers usually cost around 200-400 dollars, while more advanced filament 3D printers are 800-1000 dollars.
The only other thing that must be paid for is the main material of the printer: plastic filament. The filament is usually 20 dollars per 1kg spool, and each spool can last more than 20 large prints. Compared to the expensive costs of resin printing, filament-based 3D printing is much easier on your budget, as the printer and filament are the only investments you’ll have to make.
Winner: Filament
Summary
Overall, Filament-based 3D printing and Resin-based 3D printing both have their specialties as well as their own setbacks. Resin-based 3D printing offers future reliability in high precision and high accuracy models, while also being relatively quick to produce models. Meanwhile, filament-based 3D printing offers an easier way of printing models, without spending as much money.
The type of printer that would be best for you depends completely upon your use and restrictions. If you are a complete beginner, filament-based 3D printers are by far a better choice because of their ease of use and friendly budget. If you consider yourself an expert in 3D printing and want to level up to more accurate and precise models, then Resin-based 3D printing is the best way to do so.