What does a 3D Printer do?
Let’s take a look at a regular printer. Printing something on a regular ink-based printer requires following a process. First, you have to create the file you want to print. This could be an essay, a report, a screenplay, some pictures for a collage, basically anything that could be on paper. The next step is simply uploading your media to the printer wirelessly or by a connection cable. The printer will use this file and copy its contents onto a piece of paper. It does this using ink, the material used in the actual physical creation of whatever you’re printing.
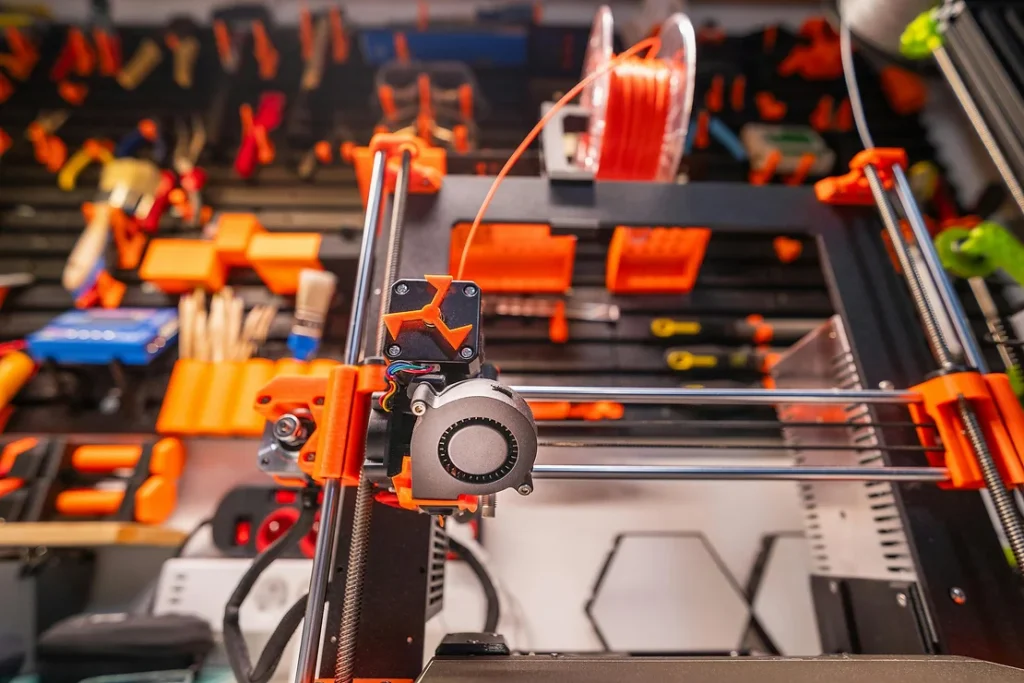
3D printers use the same process as regular printers. First, you have to create the file you want to print. This time instead of a two-dimensional design or text, the file is a three-dimensional object model. This could be a model of a product, a part of a machine, or as most hobbyists prefer, something that just looks pretty cool. After creating the 3D model, the next step is, like a regular printer, uploading the file to the printer. After the file is sent, the only thing left to do is to watch your creation being printed.
Of course, there are still many differences between regular printers and 3D printers. While regular printers use ink, 3D printers use a material called filament. Filament allows 3D printers to print in three dimensions, not just two. But we’ll talk about filament later. Another difference between the two types of printers is the outcomes of prints. Printing using regular printers results in a text or graphic design on a piece of paper. Meanwhile, 3D printing results in three-dimensional tangible objects.
How is 3D Printing Used in the Real World?
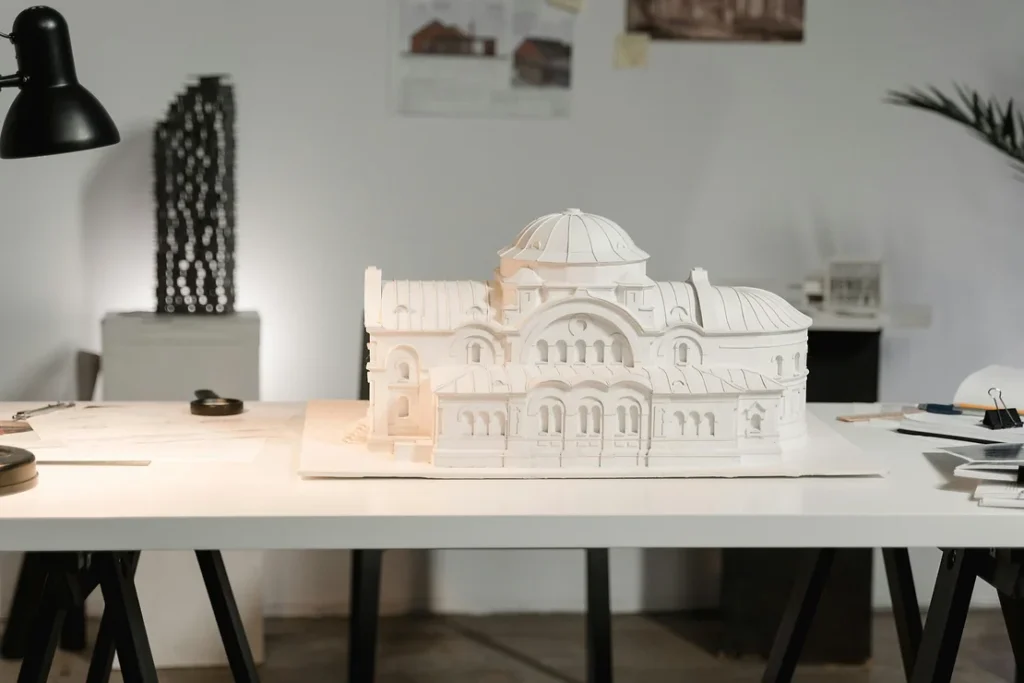

3D printing is used in numerous different industries around the world. Most industries use 3D printing for prototyping, or creating models of a product to test its effectiveness.
The automotive industry is an example of an industry that uses 3D printing for prototyping. Many companies print models of automobile parts and components to ensure the correct dimensions and functions. For example, an automobile manufacturing company can 3D print a scale model of a wheel to ensure the model is the correct size for the car.
Mechanical engineers also use 3D printing in very similar ways to the automotive industry. While automotive engineers use 3D printing for prototyping car parts and components, mechanical engineers use 3D printing to prototype mechanical parts. In some cases, this could be automobile components as well.
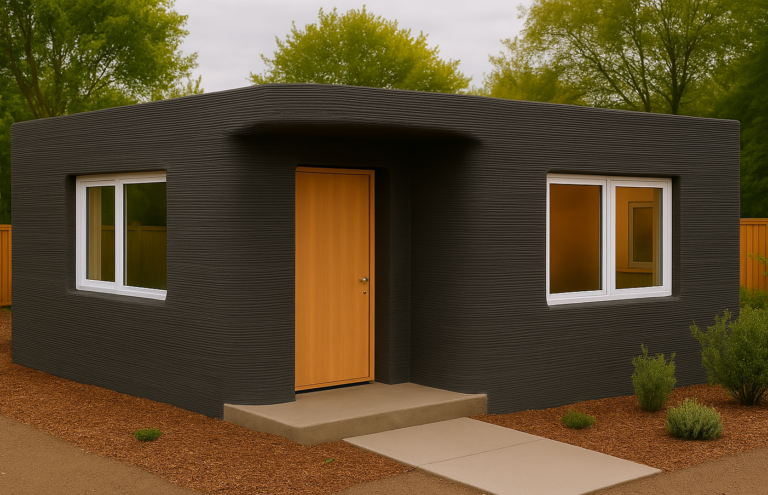
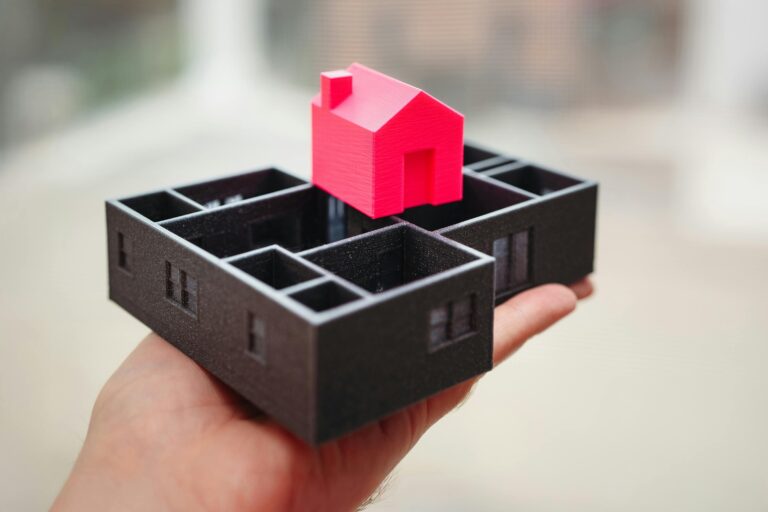
Many architectural projects also use 3D printing for prototyping. If a company is working on an architectural project, like an office building or a house, 3D printing is often used to create smaller models of the creation. Architects do this to easily showcase how their creation will look once completed.
As well as just prototyping models of products, companies can also use 3D printing techniques for manufacturing actual products. An example of this is the healthcare industry, specifically the biotechnology industry. Companies that are a part of this industry often use 3D printing when manufacturing prosthetics like prosthetic arms, legs, and more. While the material differs entirely from the commonly used PLA Filament, the practice of 3D printing is still applied in many areas of the healthcare industry.
What Is Filament?
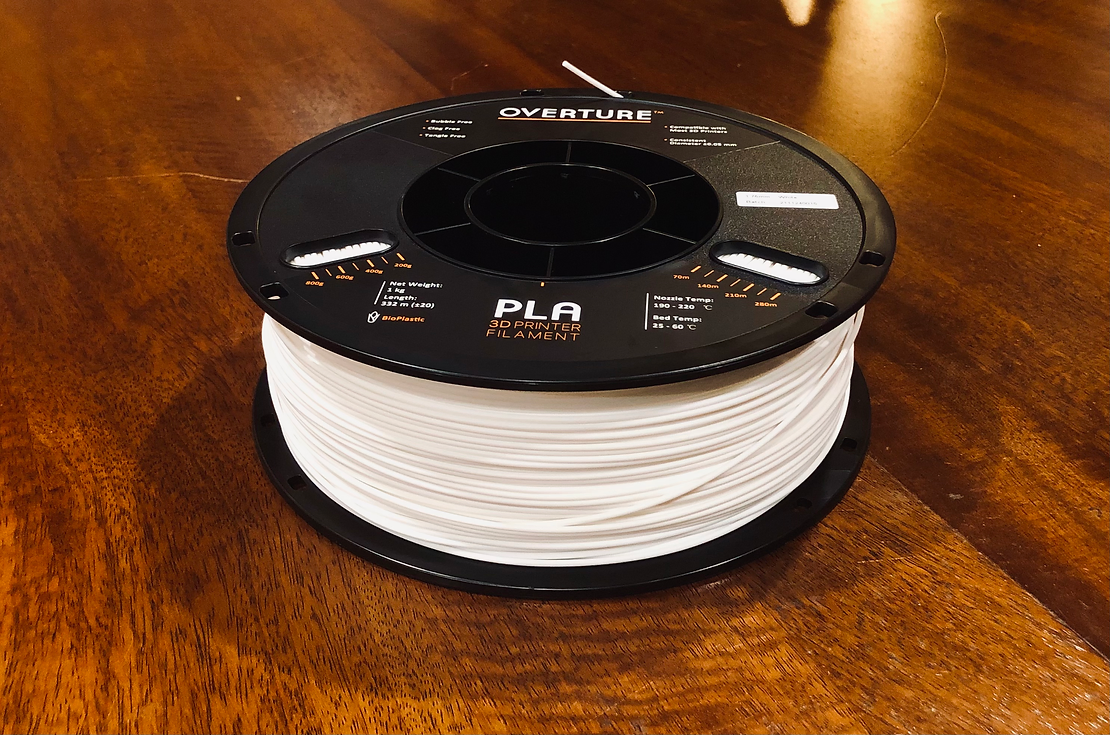

Let’s go back to the comparison of 3D printers to regular printers. In simple terms, filament acts as the “ink” of 3D printers. In normal printers, ink is used as the material being spent to create the print. 3D printing filament works in the same way, acting as the material being put together to create the object.
The most commonly used filament is PLA filament. The acronym “PLA” stands for “Polylactic Acid”. This type of filament is 100% recyclable and made from sugar cane, corn starch, and other organic and sustainable resources. PLA is a bioplastic, meaning while it isn’t created the same way most traditional plastics are, it still has the same qualities, a similar feel, and similar durability to those plastics.
This material is often used by hobbyists or by industry workers for prototyping. A model of a product doesn’t require the same durability as the manufactured product, making PLA filament a safe and efficient material for product models. Companies that use 3D printing for manufacturing, like those working in the biotechnology industry, often use a stronger material rather than traditional PLA filament
Summary
While we compared 3D printing to regular printing in the beginning, we can now see how 3D printing includes so many more capabilities and opens doors to countless opportunities in almost any industry. We learned about the process of 3D printing, and how it compares and contrasts to the process of regular printing. We explored the different fields that incorporate 3D printing, for prototyping and manufacturing, into their process of creation. And finally, we introduced filament and showcased the purpose that it has in the 3D printing process.
This post acts as a starting point for beginners ready to dive into the world of 3D printing. In the next part of this series on the Introduction to 3D printing, we’ll take a closer look into the parts and components of 3D printers, including the impact and purpose of each component.