3D printing technology has revolutionized the manufacturing process of hundreds of industries. Among the different types of 3D printing methods, resin 3D printing, or SLA printing, has emerged as a powerful tool for creating detailed and precise models. Today, we will explore the fundamentals of resin 3D printing, its materials and processes, and how it compares to traditional filament printing methods.
What is Resin 3D Printing?

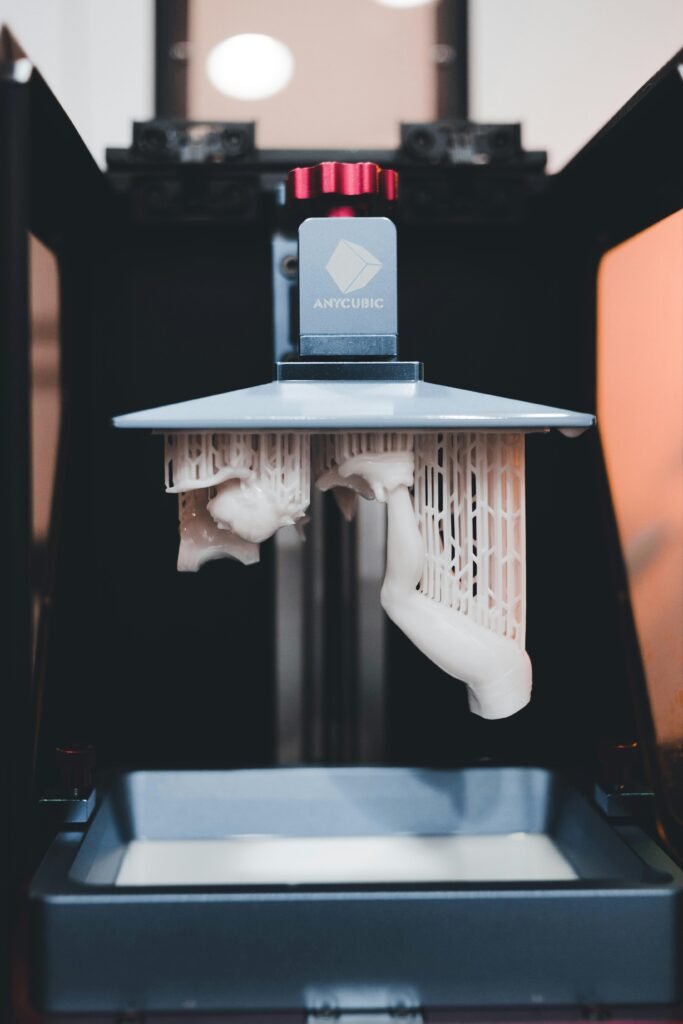
Resin 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that uses liquid UV plastic resin to create three-dimensional objects. Unlike traditional FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers that use solid plastic filaments, resin printers work with liquid plastics that harden when exposed to UV light.
In FDM Printers, the filament is melted down and then placed on a print surface or print bed in layers to construct a model layer by layer. Resin printers are similar but also different. With each layer, UV light shines in a particular pattern or shape on the liquid resin. This UV light hardens the liquid resin in the same pattern that it originally shone. This creates the first layer of a resin print. Similarly to filament printers, resin printers build up objects layer by layer on the print surface.
The General Printing Process
The process begins with a vat of liquid resin and a build surface. As each layer is created, UV light is directed onto the resin in patterns that correspond to the cross-sections of the 3D model. When the UV light hits the resin, it causes the liquid to harden into a solid form. The build platform then moves up or down slightly, allowing the next layer to be created. This process continues until the entire object is formed.
Essential Materials and Equipment

Several key components are necessary for resin 3D printing:
UV Liquid Resin
UV Liquid Resin is the primary material used in resin printing, available in various colors and properties. This liquid plastic is designed to “cure” and harden when exposed to ultraviolet light. Resin-printed items are made by exposing liquid resin to UV light to harden the resin in different layers.
Resin 3D Printer
A resin 3D printer is a device that contains many parts, systems, and essential processes to make liquid resin into a 3D model. Both resin printers and filament printers exist for the same purpose but have different methods for their purpose.
Many parts of a resin 3D printer share the same purpose as a filament 3D printer. For example, both types of printers have a print or print bed to place the layered plastic on while printing.
Isopropyl Alcohol
This chemical is used for post-processing to clean prints after the printing process is finished. SLA prints are usually placed inside a container of Isopropyl alcohol. This removes any excess liquid or un-cured resin from the print, making it clean.
Advantages of Resin 3D Printing
Resin 3D printing offers several significant advantages. The most notable of these advantages is increased print quality. Resin printers can achieve much finer layer heights compared to FDM printers. This results in more edges, smoother surfaces, and therefore, more intricate details.
Another major benefit of Resin 3D Printing is its speed. The UV curing process is relatively quick, with each layer taking only seconds to solidify. Although there are hundreds, sometimes thousands of layers, all layers always take the same amount of time to cure. This differs from filament-based printers, where the time depends on the size of each layer.
Resin printing also excels at creating miniature models and small, detailed parts that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with FDM printing.
Limitations and Considerations

Despite its advantages, resin 3D printing comes with several important considerations:
Higher Costs
Both the actual 3D Printer and ongoing material costs tend to be higher than FDM printing. Liquid UV Resin is far more expensive than plastic filament, and constant refill of resin proves to be expensive. The need for regular replacement of parts like film also adds to the overall expense. Other post-processing chemicals like isopropyl alcohol also contribute to the overall price of printing and maintenance.
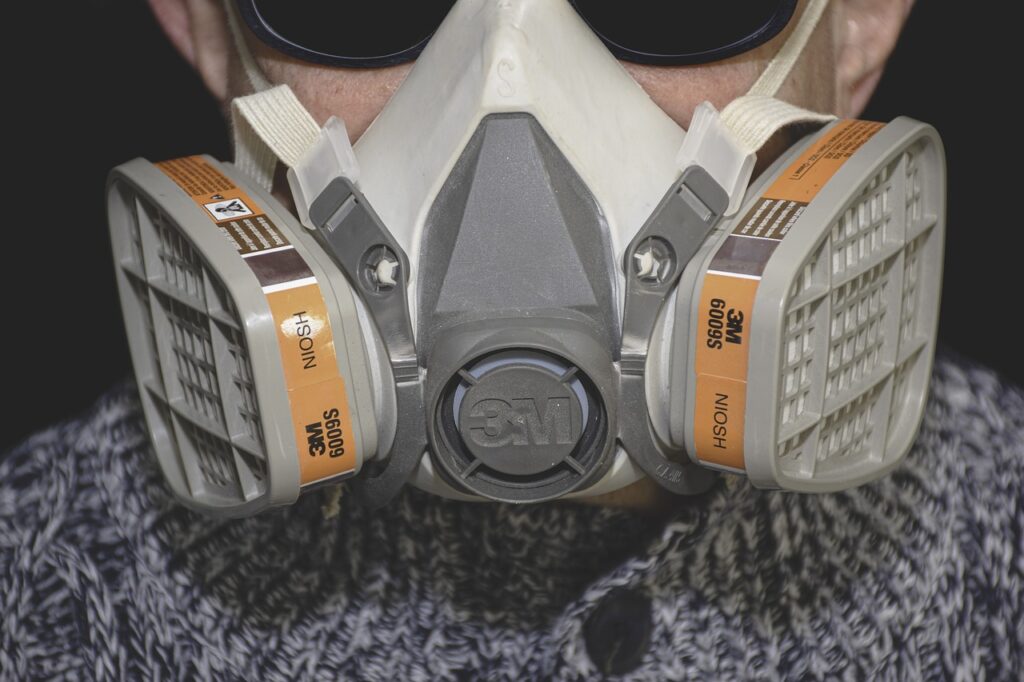
Safety Concerns
Resin printing requires very careful handling of harmful materials and chemicals. The liquid resin and cleaning chemicals can produce toxic fumes that produce strong smells and may be harmful if they come into direct contact with skin. For this reason, it is strongly advised to use safety materials like gloves, respirators, and others.
Messy Process
One of the most common complaints about resin printing is how messy it gets. The primary material, UV resin, is a hassle to move around and clean. If a print goes wrong, it’s very hard to clean the different parts of the printer. Resin also produces strong smells and fumes that linger around the printing area. Overall, constant use of a resin printer ultimately results in a very messy workspace.
Resin Printing vs. FDM Printing

While both types of 3D printing serve the same ultimate purpose of creating 3D objects, they cater to different needs. Let’s explore their specific applications in detail:
FDM Printing Applications
Large-scale objects are particularly well-suited for FDM printing. This type of 3D printing excels at creating objects like architectural models, furniture prototypes, and large mechanical parts. The build volume of FDM printers typically ranges from 500 to 1000 cubic centimeters, with some industrial models offering even larger capacities.
Costs are another major advantage of FDM printing. The actual 3D printer is generally lower, starting around $200-300 for entry-level models. Additionally, filament materials are relatively inexpensive compared to liquid resin. Standard PLA filament costs approximately $20-30 per kilogram, making it ideal for affordable projects.
When extreme detail isn’t crucial, FDM printing provides a practical solution. While layer lines may be visible, filament 3D printing is perfect for functional prototypes, basic models, and everyday objects that don’t require the most precision.
Home use is another area where FDM printing shines. These printers typically require minimal ventilation and can be safely operated in home workshops or offices. Unlike resin, most common filaments like PLA don’t emit dangerous fumes and don’t require special safety equipment. The only safety hazard while printing with filament is the extremely hot nozzle. Other than that, FDM printing is far safer than resin printing.
Resin Printing Applications
Highly detailed miniature models are where resin printing excels over FDM printing. Resin printing can produce incredibly fine details in small objects. This makes it perfect for creating tabletop character figures, jewelry prototypes, and detailed architectural models. Layer heights as small as 0.05 millimeters are possible, resulting in nearly invisible layer lines.
Engineering parts that require precision benefit greatly from resin printing capabilities. The accuracy and surface finish achieved make it great for creating prototypes of small mechanical components, dental models, and other parts requiring detail.
Professional applications requiring smooth finishes find their solution by printing with resin. The technology is particularly valuable in industries like jewelry design, dental prosthetics, and medical modeling, where surface quality and accuracy are vital.
Speed and efficiency are other strengths of resin printing. The quick layer curing time and excellent detail reproduction make it perfect for iterating through design prototypes quickly while maintaining the best quality results.
Conclusion
Resin 3D printing represents a significant advancement in additive manufacturing technology, offering unprecedented levels of detail and precision for small-scale objects. While it comes with its own set of challenges, including high costs and safety considerations, its ability to produce high-quality, detailed prints makes it a valuable tool for professionals. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of resin printing is crucial for choosing the right printing method for your own needs.